B-Cubed is delighted to share that the project has partially contributed to the publication of a new paper – Uniformly sampling pseudo-absences within the environmental space for applications in habitat suitability models. One of the authors of the paper – Duccio Rocchini – is part of B-Cubed’s team and a full professor at Alma Mater Studiorum University of Bologna.
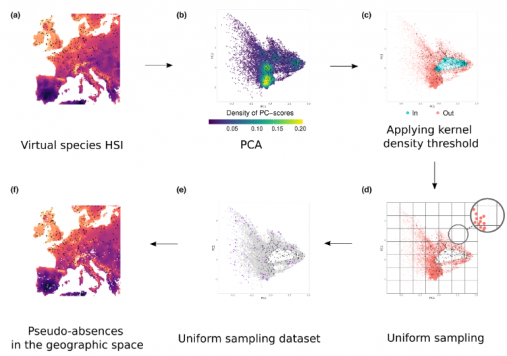
The paper introduces a novel methodology – the uniform approach – to address issues in generating pseudo-absences for habitat suitability models. By systematically sampling pseudo-absences within a portion of the environmental space delimited by a kernel-based filter, the proposed method effectively reduces sample location bias and class overlap, demonstrating comparable predictive performance while ensuring the representation of environmental conditions across the study area.
Read the full paper here.